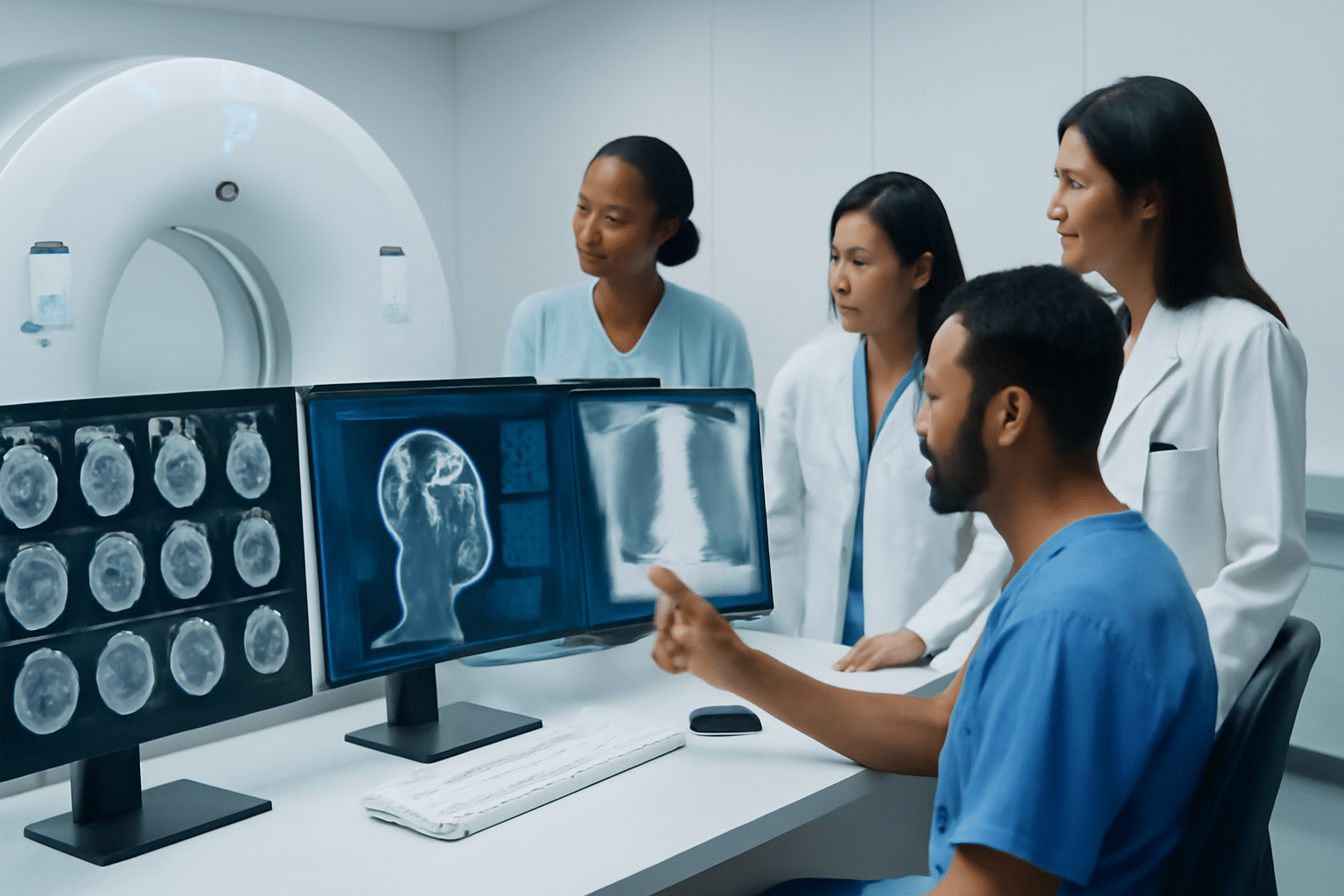
Introduction to Diag Image: What Are They and Why Do They Matter?
In today’s world of advanced medicine, diagnostic images play a crucial role in helping doctors diagnose and treat patients. But what exactly are diagnostic images, and why are they so important? Let’s break it down.
Diagnostic images are visual tools used by healthcare professionals to observe, analyze, and interpret the condition of internal organs and tissues. These images help doctors make accurate diagnoses without needing invasive procedures. From X-rays to MRIs, each type of diagnostic image serves a specific purpose, and understanding these tools can give you a clearer picture of how your health is being monitored.
What Are Diag Image?
Simply put, diagnostic images are pictures that show the inside of your body. These images are taken using different types of machines that use various technologies, such as radiation, magnets, or sound waves, to create clear pictures of your organs, bones, and tissues.
Ever wondered how doctors figure out what’s wrong inside your body without making a single cut? That’s where diagnostic imaging steps in.
Why Are Diagnostic Images So Important?
They’re game-changers in medicine for several reasons:
- Non-invasive: Instead of performing surgery or making incisions, diagnostic images allow doctors to get a detailed view of your internal health without any cutting. This makes it less painful and quicker for you to get the answers you need.
- Early detection: Many diseases, such as cancer, can be caught early with the help of diagnostic images. The sooner a condition is detected, the sooner treatment can start.
- Accurate diagnosis: With images like MRIs and CT scans, doctors can see exactly what’s happening inside your body, leading to more precise diagnoses.
How Does It Work?
Imagine an X-ray machine or an MRI scanner as your window to the inside of your body. When you’re having an X-ray, the machine sends a small amount of radiation through your body, and the denser tissues (like bones) absorb more radiation, showing up white on the image. In contrast, an MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of your organs and tissues, especially soft tissues like muscles and the brain.
Ever wondered how an MRI can capture such detailed images? Let’s dive deeper into the technology behind these fascinating images.
What Are the Different Types of Diagnostic Images?
Diagnostic images come in many shapes and forms, each tailored to specific needs in medical imaging. But what are these different types of diagnostic images, and how do they work? Let’s break down the most commonly used types.
1. X-ray Images
X-rays are one of the oldest and most widely used types of diagnostic imaging. They are particularly helpful for examining bones and detecting fractures. But how does it work?
- How does X-ray imaging work?
X-rays use a small amount of radiation to pass through the body, with denser materials (like bones) blocking more of the radiation, making them show up as white on the image. Softer tissues, like muscles and organs, allow more radiation to pass through, showing up in shades of gray.
FAQ: What is an X-ray used for?
X-rays are commonly used to check for broken bones, monitor lung conditions (like pneumonia), and look for signs of tumors or infections.
2. MRI Images (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI is a powerful diagnostic tool that uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce high-quality images of soft tissues in the body, such as the brain, spinal cord, and muscles.
- How does MRI imaging work?
MRI machines use magnets to align the atoms in your body, and then they send radio waves to disturb this alignment. As the atoms return to their original positions, they release energy, which is captured by the machine to form detailed images.
FAQ: Why would I need an MRI?
MRIs are typically used when doctors need detailed images of soft tissues, like the brain, spinal cord, or muscles, to diagnose issues such as brain tumors, spinal injuries, or joint problems.
3. CT Scan Images (Computed Tomography)
CT scans, also known as CAT scans, combine multiple X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional views of the body, providing a 3D image.
- How does CT scan imaging work?
A CT scan takes many X-ray images from different angles and combines them using a computer. This creates detailed, cross-sectional images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues, helping doctors diagnose conditions like cancer, internal bleeding, and heart disease.
FAQ: When is a CT scan used?
A CT scan is often used in emergency situations to quickly identify injuries, detect cancer, or find internal bleeding.
4. Ultrasound Images
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of organs and structures inside the body, making it the go-to method for monitoring pregnancy and evaluating organs like the heart and liver.
- How does ultrasound imaging work?
An ultrasound machine sends high-frequency sound waves through the body, and the waves bounce back from tissues to create an image. This is non-invasive and doesn’t require radiation, making it safe for regular monitoring.
FAQ: How do doctors use ultrasound during pregnancy?
Ultrasound is commonly used in pregnancy to monitor fetal development, check for abnormalities, and determine the baby’s position before birth.
Why Knowing About Diagnostic Imaging Matters
You might be asking, “Why does all this matter to me?” Well, understanding the different types of diagnostic images can help you make informed decisions about your health. Whether it’s determining whether you need an MRI for joint pain or getting an X-ray for a potential fracture, knowing how these technologies work can help you feel more confident about the procedures.
Each imaging type has its strength, depending on what your doctor needs to see. So next time you’re scheduled for an imaging test, you’ll have a clearer idea of why it’s being recommended.
The Role of Diagnostic Imaging in Disease Detection and Treatment
Diagnostic imaging isn’t just about taking pictures of the inside of the body—it plays a vital role in diagnosing diseases, detecting problems early, and guiding treatment decisions. So, how exactly does diagnostic imaging help in disease detection and treatment?
1. Early Detection of Diseases
One of the greatest strengths of diagnostic imaging is its ability to detect diseases at an early stage—sometimes even before symptoms appear. Early detection means that treatment can start sooner, which often leads to better outcomes.
- Why is early detection important?
The earlier a disease is found, the easier it is to treat, especially when it comes to conditions like cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
Real-life example: Breast cancer, when caught early through mammograms (a form of diagnostic imaging), can often be treated more effectively, saving lives and reducing the need for invasive treatments.
FAQ: Can diagnostic imaging help detect cancer?
Yes, diagnostic imaging is key to early cancer detection. Mammograms, CT scans, and MRIs are commonly used to find tumors and identify early-stage cancers.
2. Monitoring Disease Progression
Once a disease has been diagnosed, diagnostic imaging is incredibly useful for tracking its progression. Whether it’s cancer, arthritis, or heart disease, imaging allows doctors to see how a condition is evolving and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- How does it help in monitoring?
Imaging tests are often repeated over time to check if a disease is growing, spreading, or improving with treatment. This gives doctors a clear picture of how well a patient is responding to medications, surgery, or other treatments.
Real-life example: In cancer patients, doctors use diagnostic imaging to monitor the size of tumors and ensure that chemotherapy is working to shrink them.
FAQ: How does diagnostic imaging help in monitoring cancer treatment?
Doctors use CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans to track how tumors respond to treatment. If a tumor shrinks, that’s a good sign that the treatment is working.
3. Guiding Treatment Decisions
Imagine having to make a crucial decision about your treatment without the right tools. That’s where diagnostic imaging comes in—it gives healthcare providers the detailed insights they need to make informed, accurate treatment decisions.
- Why is it essential for treatment planning?
For instance, before surgery, doctors use diagnostic images to determine the exact location of a problem and plan the most effective surgical approach. Similarly, imaging helps guide radiation therapy to ensure it targets the right areas.
Real-life example: Before performing surgery on a brain tumor, a doctor will use an MRI to locate the tumor’s size and position. This ensures that the surgery is as precise and safe as possible.
FAQ: How does an MRI influence treatment decisions?
An MRI provides a detailed view of soft tissues like the brain, spinal cord, and muscles, allowing doctors to plan surgeries or non-invasive treatments accurately, reducing the risk of complications.
4. Improving Patient Outcomes with Diagnostic Imaging
The ultimate goal of diagnostic imaging is to improve patient outcomes, whether it’s by detecting a disease early, tracking its progress, or guiding treatments. Accurate imaging leads to faster, more targeted treatments, which significantly improves a patient’s chances of recovery.
- How does diagnostic imaging improve outcomes?
With the right imaging tools, healthcare providers can identify problems early, personalize treatment plans, and minimize unnecessary procedures, all of which contribute to a quicker, safer recovery for patients.
Real-life example: In emergency care, a CT scan can quickly identify internal bleeding or fractures, allowing doctors to act fast and prevent further harm.
FAQ: How does diagnostic imaging improve patient care?
Diagnostic imaging allows healthcare providers to see inside the body in real-time, leading to faster diagnoses, more personalized treatment plans, and better outcomes.
The Technologies Behind Diagnostic Imaging: Advancements and Innovations
As technology evolves, so does the field of diagnostic imaging. From traditional X-rays to cutting-edge MRI machines, diagnostic imaging has come a long way. But what are the latest advancements, and how are they shaping the future of healthcare? Let’s dive into the technologies that power these incredible tools.
1. The Evolution of Diagnostic Imaging Technology
Diagnostic imaging has evolved significantly over the past century. Early on, simple X-rays were the primary imaging tool used in medicine. But today, we have a range of advanced technologies that provide highly detailed and accurate images.
- The shift from film to digital imaging
In the past, X-ray images were captured on film, which needed to be developed manually. Today, most imaging is digital, which makes it faster, easier, and more accessible. Digital imaging also allows for easier storage, retrieval, and sharing of images between healthcare providers.
FAQ: Why is digital imaging better than traditional film?
Digital imaging is faster, more accurate, and offers better image quality. It also allows healthcare providers to store and access images electronically, making the entire process more efficient.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostic Imaging
AI is making waves across healthcare, and diagnostic imaging is no exception. Machine learning algorithms can now analyze medical images with remarkable accuracy, sometimes even detecting subtle abnormalities that a human eye might miss.
- AI’s role in image analysis
AI is used to speed up the analysis of diagnostic images. For instance, AI-powered tools can quickly scan CT scans or MRIs and highlight areas of concern, allowing doctors to focus on critical findings. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of human error.
Real-life example: In radiology, AI tools are helping doctors identify tumors or heart conditions more accurately by analyzing the images and suggesting areas for further examination.
FAQ: How is AI used in diagnostic imaging?
AI algorithms can analyze medical images for patterns, helping detect conditions like cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders more accurately and quickly than manual analysis.
3. 3D Imaging and Advanced MRI Techniques
3D imaging is transforming how we see the body’s internal structures. By combining multiple 2D images, advanced MRI and CT scans can now create detailed 3D models, providing a more comprehensive view of the body.
- The power of 3D imaging
3D imaging is especially useful in planning surgeries or assessing complex conditions. Surgeons can view organs, blood vessels, and tumors in three dimensions, allowing for more precise and less invasive surgeries.
Real-life example: Surgeons can use 3D imaging to plan complex spinal surgeries or brain surgeries, improving their ability to target affected areas while minimizing risks.
FAQ: What is the advantage of 3D imaging in diagnostics?
3D imaging provides a more detailed and accurate view of the body’s internal structures, helping doctors make more informed decisions about treatment and surgery.
4. Portable and Point-of-Care Imaging Devices
Gone are the days when diagnostic imaging was confined to hospitals or specialized clinics. Today, portable imaging devices allow healthcare professionals to take high-quality images right at the patient’s bedside or in remote locations.
- How portable imaging works
Portable ultrasound machines and handheld X-ray devices have made it easier for doctors to perform diagnostic imaging in various settings, from emergency rooms to rural clinics. These portable tools are revolutionizing patient care, especially in underserved areas.
Real-life example: During emergencies, doctors can use portable ultrasound devices to quickly check for internal injuries or complications, leading to faster decision-making and treatment.
FAQ: Can portably imaging devices be as effective as traditional machines?
Yes, portable imaging devices are often just as effective as traditional ones, providing high-quality images. However, their convenience and accessibility make them even more valuable in urgent or remote situations.
5. The Future of Diagnostic Imaging: What’s Next?
The future of diagnostic imaging looks incredibly promising. With new technologies constantly emerging, we can expect even more precise, efficient, and patient-friendly imaging solutions.
- Next-gen imaging technologies
Future advancements may include imaging devices that are even more portable, faster, and capable of providing real-time results. Innovations like AI-assisted imaging, better 3D models, and even molecular imaging are paving the way for a more personalized and effective healthcare experience.
FAQ: What’s the next big thing in diagnostic imaging?
We can expect AI to play a larger role, with more AI-powered imaging tools capable of detecting diseases earlier and with greater precision. Additionally, advancements in molecular imaging may allow for even earlier detection of conditions at the cellular level.
Ethical Considerations and Safety in Diagnostic Imaging
While diagnostic imaging has revolutionized healthcare, it’s essential to address the ethical and safety concerns associated with these technologies. Let’s explore the key issues and how the medical community ensures that diagnostic imaging is used responsibly and safely.
1. Ethical Issues in Diagnostic Imaging
As with any medical procedure, diagnostic imaging comes with ethical considerations, especially regarding patient privacy, consent, and the appropriate use of technology.
- Informed consent
Before undergoing any imaging procedure, it’s important that patients understand the risks and benefits. Informed consent ensures that patients are aware of what the procedure involves and any potential side effects.
Real-life example: For an MRI scan, patients are asked to sign a consent form acknowledging the procedure, its purpose, and any potential discomforts or risks, like claustrophobia or noise.
FAQ: Why is informed consent important in diagnostic imaging?
Informed consent ensures that patients understand the risks and benefits of diagnostic tests, allowing them to make well-informed decisions about their care.
- Privacy and data protection
Diagnostic images contain highly sensitive information about a person’s health. Proper handling, storage, and sharing of these images are crucial to protect patient privacy. Medical facilities are required to follow strict guidelines under laws like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) to ensure that patient data remains confidential.
FAQ: How is patient data protected in diagnostic imaging?
Hospitals and clinics store diagnostic images electronically in secure systems. These images are only accessible to authorized medical personnel, ensuring that patient privacy is maintained.
2. Safety Considerations in Diagnostic Imaging
While diagnostic imaging is generally safe, certain procedures—especially those involving radiation—do come with potential risks. Understanding these risks and the safety measures in place is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Radiation exposure
Some diagnostic imaging techniques, like X-rays and CT scans, involve radiation. Although the levels of radiation used are usually low, excessive exposure over time can increase the risk of developing cancer. That’s why doctors always carefully weigh the benefits and risks before recommending such imaging procedures.
Real-life example: Pregnant women are often advised to avoid unnecessary X-rays or CT scans due to the potential risks of radiation exposure to the fetus.
FAQ: Is diagnostic imaging safe?
Yes, diagnostic imaging is safe when performed appropriately. Doctors carefully consider the risks, especially with radiation-based imaging, to minimize any potential harm.
- Minimizing risks
New technologies and safety protocols are constantly being developed to reduce radiation exposure. For example, advanced CT scan machines use lower doses of radiation, while modern X-ray equipment is more efficient, reducing the overall exposure.
FAQ: How is radiation exposure minimized in imaging?
Modern imaging technologies use lower doses of radiation without compromising the quality of the images, ensuring that patients receive the necessary diagnostic information while minimizing risk.
3. The Role of the Healthcare Provider in Ensuring Safety
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in ensuring the safety of patients during diagnostic imaging procedures. From explaining the procedure and its potential risks to following safety protocols, medical staff are trained to prioritize patient well-being at every stage of the imaging process.
- Radiology technicians and safety
Radiology technicians are specially trained to operate imaging equipment safely. They take precautions to protect both the patient and themselves from unnecessary radiation exposure.
Real-life example: Before performing an X-ray, the technician may place a lead apron on the patient to protect vital organs from radiation, ensuring that only the necessary area is exposed.
FAQ: How do radiology technicians ensure safety during imaging?
Radiology technicians follow strict safety protocols, including using protective gear, adjusting equipment settings to minimize radiation, and ensuring the patient is positioned correctly.
4. Ethical Use of Advanced Technologies in Diagnostic Imaging
With advancements like AI in diagnostic imaging, the ethical concerns surrounding the use of artificial intelligence in medicine are becoming increasingly important. AI tools must be transparent, unbiased, and thoroughly tested to ensure they enhance, rather than replace, human judgment.
- Transparency and accountability in AI
It’s essential that healthcare providers understand how AI algorithms work and ensure that these tools don’t replace the need for expert human interpretation. AI should be used to support, not override, the decisions of trained healthcare professionals.
FAQ: Can AI be trusted in diagnostic imaging?
AI is a valuable tool for assisting doctors in interpreting images, but it is not infallible. It should always be used alongside human expertise to ensure the best outcomes for patients.
- Addressing biases in AI algorithms
Since AI algorithms are trained on large datasets, it’s essential that these datasets are diverse and representative of different populations. This helps prevent biases that could lead to misdiagnoses or unequal treatment of certain groups.
FAQ: Can AI algorithms be biased in diagnostic imaging?
Yes, AI algorithms can be biased if they are trained on incomplete or non-representative data. Healthcare providers must ensure that AI tools are tested and refined to reduce any potential biases.
The Future of Diagnostic Imaging: What’s Next?
The world of diagnostic imaging is evolving rapidly, with technological advancements constantly shaping the way we detect and treat diseases. But what’s on the horizon for this essential tool in modern medicine? Let’s take a closer look at the exciting future developments and how they’ll impact healthcare.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Imaging
We’ve already seen how AI is enhancing diagnostic imaging, but it’s just the beginning. In the future, AI is expected to play an even larger role in automating image analysis, offering greater accuracy, speed, and efficiency.
- AI in automated image interpretation
AI algorithms are becoming better at analyzing medical images, detecting patterns, and diagnosing conditions faster than human radiologists. These tools could reduce human error and provide quicker results, especially in time-sensitive situations like emergency care.
Real-life example: In some hospitals, AI is already used to analyze chest X-rays for signs of pneumonia. The AI algorithm can spot potential issues in seconds, providing doctors with a starting point for further examination.
FAQ: How will AI change the way doctors use diagnostic images?
AI will assist doctors by automating the initial analysis of images, saving time and allowing medical professionals to focus on more complex tasks that require human judgment.
2. Portable and Point-of-Care Diagnostic Imaging
Advancements in portability are making diagnostic imaging more accessible than ever before. Soon, we can expect to see more handheld imaging devices that allow doctors to perform diagnostic imaging on the go, in any setting.
- Portable ultrasound machines
Portable ultrasound devices have already revolutionized areas like obstetrics, where expectant mothers can get ultrasound scans right in the doctor’s office or even at home in some cases. This trend is expected to expand to other imaging modalities like X-rays and MRIs, making healthcare even more accessible.
Real-life example: Emergency responders are now able to use portable ultrasound devices in ambulances to check for internal injuries in trauma patients before they even arrive at the hospital, speeding up treatment.
FAQ: Are portable imaging devices as reliable as traditional machines?
Yes, portable imaging devices can provide high-quality images that are just as reliable as traditional, stationary machines. They offer the advantage of flexibility and quick access, especially in emergency situations.
3. 3D and 4D Imaging Technologies
The evolution from 2D to 3D imaging has already made significant strides in diagnostic imaging, and soon, 4D imaging will take things even further. These technologies are set to provide incredibly detailed views of organs, tissues, and even blood flow in real-time.
- The power of 3D and 4D imaging
3D imaging is already used in planning surgeries and assessing complex conditions. With 4D imaging, doctors will be able to visualize not just the static structures of the body, but also the dynamic processes like blood flow and organ movement over time.
Real-life example: Surgeons could use 4D imaging to track the movement of a tumor in real-time during surgery, ensuring that it is removed with precision while avoiding damage to surrounding tissues.
FAQ: What is 4D imaging, and how is it different from 3D?
4D imaging takes 3D imaging a step further by adding the element of time, allowing doctors to see how organs and tissues move or change over time. This is especially useful in fields like cardiology and oncology.
4. Molecular and Genomic Imaging
Looking even further ahead, molecular and genomic imaging techniques are poised to revolutionize early disease detection. These techniques allow doctors to observe cellular and molecular changes in the body, offering a glimpse into the earliest stages of disease, even before symptoms appear.
- Molecular imaging for early disease detection
This technique uses imaging agents to target specific molecules or cells in the body, providing highly detailed images of molecular activity. For instance, molecular imaging is already being used in cancer research to identify tumor markers and track the spread of cancer cells.
Real-life example: In cancer treatment, molecular imaging can show how well a patient’s tumor is responding to treatment by targeting the cancer cells with a radioactive tracer.
FAQ: What is molecular imaging, and how does it work?
Molecular imaging involves using tracers that bind to specific molecules in the body, enabling doctors to visualize the activity of these molecules. This helps in early disease detection and monitoring the effectiveness of treatments.
5. Virtual and Augmented Reality in Diagnostic Imaging
Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies are also making their way into diagnostic imaging, offering immersive experiences that can aid in diagnosis, treatment planning, and education.
- How VR and AR are changing diagnostic imaging
By using VR and AR, doctors can “walk through” 3D images of a patient’s internal structures, offering a better understanding of complex conditions. These technologies can also be used in training, allowing medical students to practice diagnosing and treating virtual patients.
Real-life example: Surgeons can use AR glasses to overlay 3D images of a patient’s organs directly onto their bodies during surgery, improving precision and reducing the risk of errors.
FAQ: How will VR and AR help doctors in diagnosing patients?
VR and AR will provide doctors with immersive, 3D views of a patient’s anatomy, allowing for better visualization and planning of complex surgeries or treatments.
Conclusion: How Diagnostic Imaging is Shaping the Future of Healthcare
As we’ve seen throughout this article, diagnostic imaging is a cornerstone of modern healthcare. From its early use in detecting fractures to its role in identifying cancer and monitoring treatment progress, diagnostic imaging has evolved to become an indispensable tool for doctors and patients alike. But the story doesn’t end here—it’s just the beginning.
The Continuous Evolution of Diagnostic Imaging
Every year, new advancements and breakthroughs bring us closer to more precise, efficient, and accessible healthcare. The future of diagnostic imaging promises even greater improvements, from AI-driven analysis to portable, point-of-care devices. These innovations will continue to push the boundaries of what we can detect and treat, leading to better health outcomes for millions of people around the world.
- AI and machine learning will reduce human error, speed up diagnoses, and even assist doctors in finding problems that might otherwise be missed.
- Portable diagnostic devices will make healthcare more accessible, especially in emergency situations or remote areas.
- Molecular and 3D imaging will allow doctors to see even deeper into the body, providing earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
Why Understanding Diagnostic Imaging is Essential for You
Knowing how diagnostic imaging works—and how it’s evolving—empowers you as a patient. Whether you’re preparing for an MRI, a CT scan, or an ultrasound, understanding what’s involved helps reduce anxiety and increases confidence in the healthcare process. Moreover, with advancements in these technologies, you can expect more personalized, quicker, and less invasive treatments.
- Informed decisions: When you understand what diagnostic imaging is, how it works, and what technologies are available, you can make more informed decisions about your healthcare.
- Better health outcomes: The more we know about these tools, the better equipped we are to use them for preventative care and early disease detection, leading to better health outcomes.
Final Thoughts: The Impact of Diagnostic Imaging
In a world where healthcare is constantly evolving, diagnostic imaging stands out as one of the most powerful tools in modern medicine. It allows doctors to see what’s happening inside your body without the need for invasive procedures. With ongoing advancements, it’s clear that diagnostic imaging will continue to be a game-changer in the fight against diseases, offering patients faster, more accurate, and less invasive treatments.
So, the next time you’re scheduled for an imaging test, you’ll know just how crucial this technology is to your healthcare journey. It’s more than just a tool—it’s a lifeline to better, more effective care.